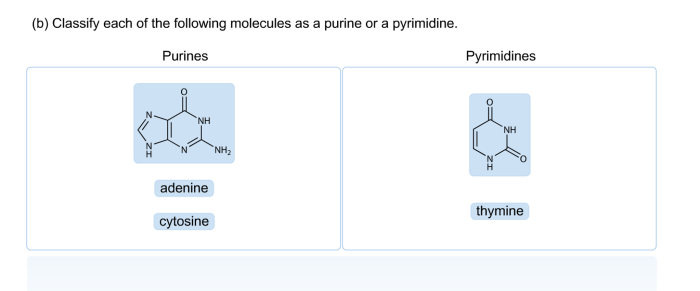
Classify each molecule as a purine or a pyrimidine, an essential step in understanding the structure and function of DNA and RNA. Purines and pyrimidines are the nitrogenous bases that form the building blocks of these essential biomolecules. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of their chemical structures, classification methods, and biological significance.
Purines and pyrimidines are classified based on their chemical structures. Purines have a double-ring structure, while pyrimidines have a single-ring structure. These differences in structure lead to distinct chemical properties and biological functions.
1. Introduction: Classify Each Molecule As A Purine Or A Pyrimidine
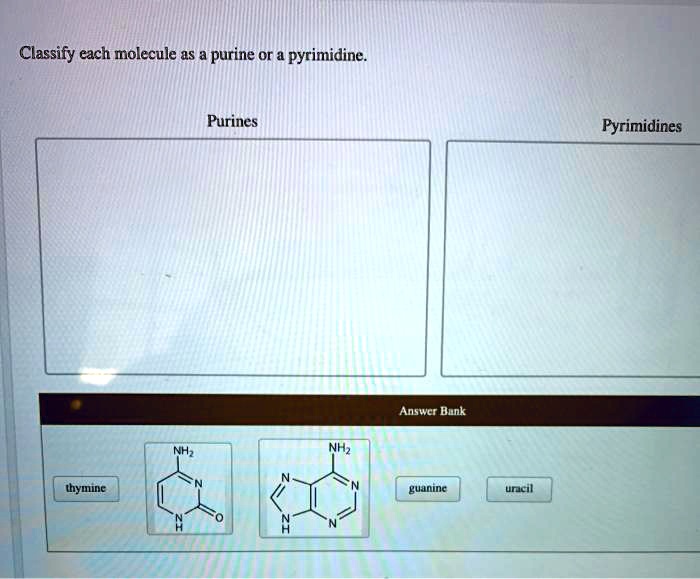
Purines and pyrimidines are two classes of nitrogenous bases that are essential components of nucleic acids, the molecules that carry genetic information. Purines include adenine and guanine, while pyrimidines include cytosine, thymine, and uracil.
These bases play a crucial role in the structure and function of DNA and RNA. They form the building blocks of nucleotides, the basic units of nucleic acids, and their sequence determines the genetic code that governs all living organisms.
2. Structural Characteristics
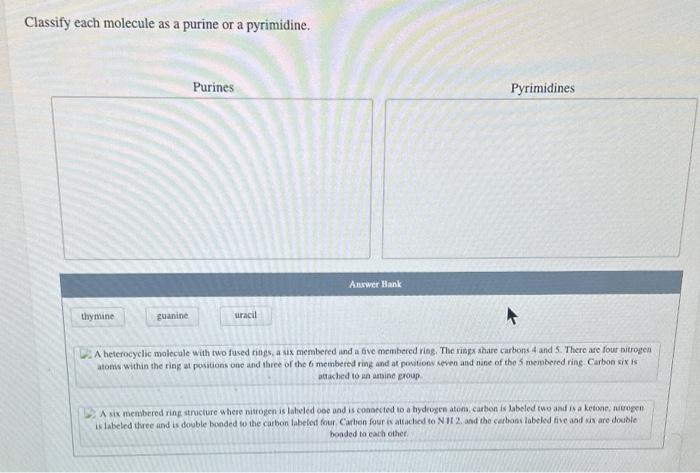
Purines
Purines have a double-ring structure consisting of a fused pyrimidine and imidazole ring. The nitrogen atoms in the purine ring are numbered N1 to N9, and the carbon atoms are numbered C2 to C8.
Pyrimidines, Classify each molecule as a purine or a pyrimidine
Pyrimidines have a single-ring structure consisting of a six-membered heterocyclic ring. The nitrogen atoms in the pyrimidine ring are numbered N1 to N3, and the carbon atoms are numbered C2 to C6.
3. Classification Methods
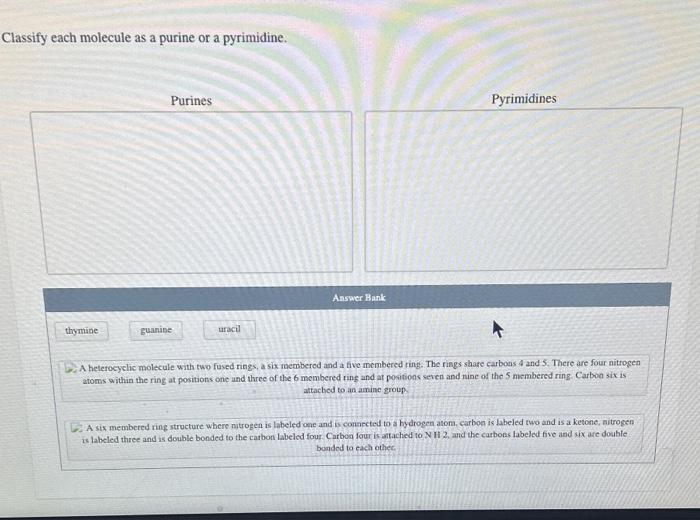
Molecules can be classified as purines or pyrimidines based on their chemical structure or spectroscopic properties.
Chemical Tests
The Bial’s test is a chemical test that can be used to differentiate between purines and pyrimidines. Purines give a positive reaction, producing a blue or green color, while pyrimidines give a negative reaction.
Spectroscopic Techniques
Spectroscopic techniques, such as ultraviolet-visible (UV-Vis) spectroscopy and nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy, can also be used to classify purines and pyrimidines based on their absorption or resonance patterns.
4. Examples and Applications
| Base | Chemical Formula | Biological Function |
|---|---|---|
| Adenine | C5H5N5 | Purine base found in DNA and RNA; pairs with thymine in DNA and uracil in RNA |
| Guanine | C5H5N5O | Purine base found in DNA and RNA; pairs with cytosine |
| Cytosine | C4H5N3O | Pyrimidine base found in DNA and RNA; pairs with guanine |
| Thymine | C5H6N2O2 | Pyrimidine base found only in DNA; pairs with adenine |
| Uracil | C4H4N2O2 | Pyrimidine base found only in RNA; pairs with adenine |
Purine and pyrimidine metabolism is essential for various cellular processes, including DNA replication, RNA transcription, and protein synthesis. Dysregulation of purine and pyrimidine metabolism has been linked to several diseases, including cancer and gout.
Popular Questions
What is the difference between a purine and a pyrimidine?
Purines have a double-ring structure, while pyrimidines have a single-ring structure.
Why is it important to classify molecules as purines or pyrimidines?
Classifying molecules as purines or pyrimidines helps us understand their chemical properties and biological functions, particularly in the context of DNA and RNA.