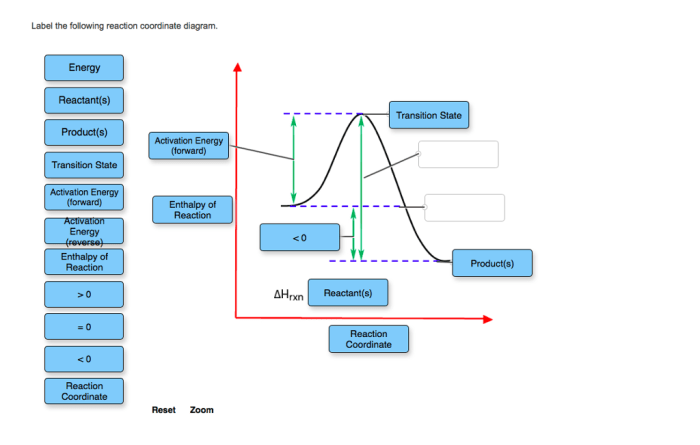
Label the following reaction coordinate diagram – As we delve into the intricacies of reaction coordinate diagrams, this introductory paragraph serves as a beacon, illuminating the path to a profound understanding of this fundamental concept. Through a meticulous exploration of its components and applications, we embark on an intellectual journey that promises to enrich our comprehension of chemical reactions.
Reaction coordinate diagrams play a pivotal role in deciphering the intricate dance of chemical reactions, providing a visual representation of the energy landscape that governs their progression. These diagrams unveil the hidden dynamics of reactions, enabling us to unravel the mysteries of activation energies, transition states, and reaction mechanisms.
Reaction Coordinate Diagrams
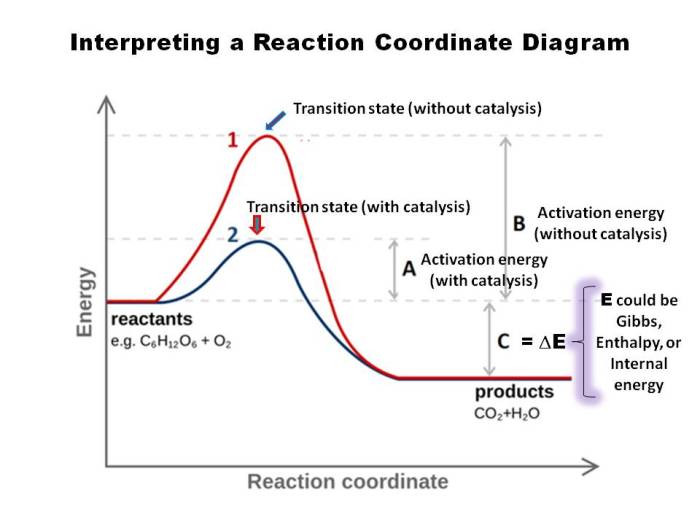
Reaction coordinate diagrams (RCDs) are graphical representations of the energy changes that occur during a chemical reaction. They are used to visualize the reaction pathway and to identify the transition states and intermediates involved in the reaction.
Overview
RCDs are constructed by plotting the potential energy of the system on the y-axis and the reaction coordinate on the x-axis. The reaction coordinate is a generalized measure of the progress of the reaction, and it can be any variable that changes during the reaction, such as the bond length, the bond angle, or the concentration of a reactant or product.
Labeling the Reaction Coordinate Diagram
The following components of a reaction coordinate diagram need to be labeled:
- The axes: The x-axis should be labeled with the reaction coordinate, and the y-axis should be labeled with the potential energy.
- The energy levels: The energy levels of the reactants, products, and transition states should be labeled on the diagram.
- The transition states: The transition states are the points on the diagram where the potential energy is at a maximum.
- The intermediates: The intermediates are the points on the diagram where the potential energy is at a minimum.
Analysis of the Reaction Coordinate Diagram, Label the following reaction coordinate diagram
The reaction coordinate diagram can be used to analyze the reaction pathway. The shape of the diagram can provide information about the activation energy, the reaction rate, and the reaction mechanism.
- The activation energy is the difference in energy between the reactants and the transition state. The higher the activation energy, the slower the reaction rate.
- The reaction rate is the rate at which the reactants are converted into products. The reaction rate is proportional to the height of the transition state.
- The reaction mechanism is the pathway by which the reactants are converted into products. The reaction mechanism can be determined by analyzing the shape of the reaction coordinate diagram.
Applications of the Reaction Coordinate Diagram
The reaction coordinate diagram is a useful tool for understanding the mechanisms of chemical reactions. It can be used in a variety of fields, including chemistry, biology, and materials science.
- In chemistry, the reaction coordinate diagram can be used to study the mechanisms of organic reactions, inorganic reactions, and gas-phase reactions.
- In biology, the reaction coordinate diagram can be used to study the mechanisms of enzyme catalysis and protein folding.
- In materials science, the reaction coordinate diagram can be used to study the mechanisms of crystal growth and phase transitions.
Questions and Answers: Label The Following Reaction Coordinate Diagram
What is the significance of labeling reaction coordinate diagrams?
Labeling reaction coordinate diagrams is crucial for accurately interpreting the energy landscape of a reaction. It allows us to identify key features such as reactants, products, transition states, and intermediates, providing a clear understanding of the reaction pathway.
How can reaction coordinate diagrams be used to predict reaction rates?
Reaction coordinate diagrams provide valuable insights into the factors that influence reaction rates. By analyzing the activation energy and the shape of the diagram, we can make informed predictions about the rate at which a reaction will proceed.