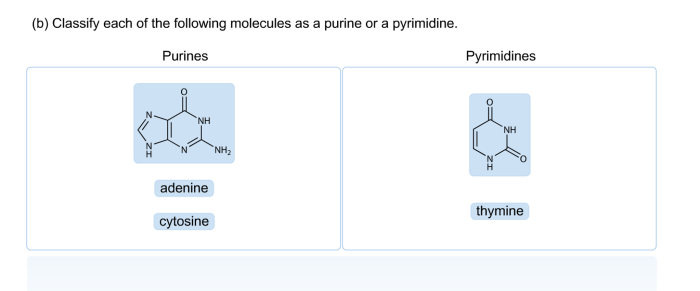
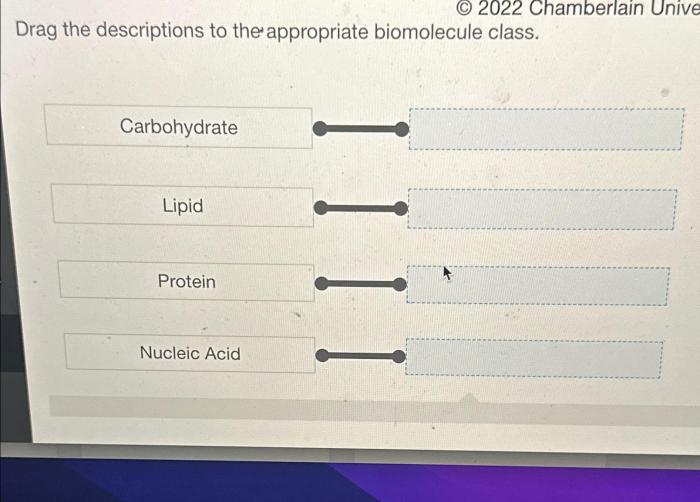
Drag the descriptions to the appropriate biomolecule class. – In the realm of biochemistry, understanding the diverse array of biomolecules and their intricate roles is paramount. Drag the Descriptions to the Appropriate Biomolecule Class offers an interactive and engaging approach to mastering this fundamental aspect of molecular biology.
This exercise provides a comprehensive overview of the major biomolecule classes—carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids—guiding learners through their unique structures, compositions, and biological functions.
Introduction to Biomolecules
Biomolecules are the building blocks of life. They are large, complex molecules that perform a variety of essential functions in living organisms. Biomolecules can be classified into four main groups: carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids.
Classifying biomolecules accurately is important for understanding their structure, function, and role in biological processes. This classification system allows scientists to organize and study biomolecules in a systematic way.
Carbohydrates
Carbohydrates are composed of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms. They are the body’s primary source of energy. Carbohydrates can be classified into three main types: monosaccharides, disaccharides, and polysaccharides.
Monosaccharides
- Simple sugars, such as glucose, fructose, and galactose
- Cannot be broken down into smaller carbohydrates
Disaccharides
- Two monosaccharides linked together
- Examples include sucrose (table sugar), lactose (milk sugar), and maltose (malt sugar)
Polysaccharides
- Long chains of monosaccharides
- Examples include starch (plants), glycogen (animals), and cellulose (plants)
Lipids
Lipids are a diverse group of biomolecules that are composed of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms. They are insoluble in water and soluble in organic solvents. Lipids can be classified into several types, including fatty acids, phospholipids, steroids, and waxes.
Fatty Acids, Drag the descriptions to the appropriate biomolecule class.
- Long chains of carbon atoms with hydrogen atoms attached
- Can be saturated (no double bonds) or unsaturated (one or more double bonds)
Phospholipids
- Lipids that contain a phosphate group
- Form the lipid bilayer of cell membranes
Steroids
- Lipids with a four-ring structure
- Examples include cholesterol, hormones, and vitamin D
Waxes
- Lipids that are composed of fatty acids and alcohols
- Provide a protective coating for plants and animals
Proteins
Proteins are composed of amino acids. They are essential for a variety of cellular functions, including metabolism, growth, and repair. Proteins can be classified into several types, including enzymes, hormones, antibodies, and structural proteins.
Levels of Protein Structure
- Primary structure: The sequence of amino acids in a protein
- Secondary structure: The folding of the protein into a specific shape
- Tertiary structure: The further folding of the protein into a specific three-dimensional shape
- Quaternary structure: The interaction of multiple protein subunits to form a functional protein
Examples of Proteins
- Enzymes: Catalyze chemical reactions in the body
- Hormones: Regulate body functions
- Antibodies: Protect the body from infection
- Structural proteins: Provide support and protection for cells and tissues
Nucleic Acids
Nucleic acids are composed of nucleotides. They are essential for storing and transmitting genetic information. There are two main types of nucleic acids: DNA and RNA.
Structure of a Nucleotide
- A nitrogenous base
- A ribose or deoxyribose sugar
- A phosphate group
Types of Nucleic Acids
- DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid): Double-stranded helix that contains the genetic code
- RNA (ribonucleic acid): Single-stranded molecule that helps to decode the genetic code and synthesize proteins
Question Bank: Drag The Descriptions To The Appropriate Biomolecule Class.
What is the significance of biomolecule classification?
Biomolecule classification is crucial for understanding the diverse roles and functions of molecules within living organisms. It provides a systematic framework for organizing and comprehending the vast array of biomolecules, facilitating targeted research and advancements in fields such as medicine and biotechnology.